The impact of solar energy in the sustainable development of the Indian Energy Industry
The demand for electricity and the electrical energy is ever increasing. New power plants are being established to meet the ever rising power demand. In this race for enhancing the power generation capacity, it is of paramount importance to build capacity in a sustainable way. The power generation source can be either through non-renewable sources or renewable sources of energy. The power generation through non-renewable source of energy leave behind lot of threat to the environment. Coal power plants emit tremendous amount of carbon dioxide which is very harmful to the environment. Since 2010, there has been a steady momentum in the solar energy industry in India and there has been lot of buzz word around the solar industry in India. Has solar energy helped the Indian energy industry to grow in a sustainable way is the answer that environmentalists look up to. This paper aims to help the readers to understand the sustainable impact of solar energy in the Indian energy industry.
SOLAR ENERGY – AN INTRODUCTION
Out of the many starts available in the galaxy, sun is the star that is responsible for the light and heat that are being utilized by the humans and the other species on the earth. Without the light and heat from the sun, the life on the earth is impossible. The gravity of the sun is also responsible for the earth to remain in its orbit. The energy from the sun is ever present and a powerful resource for the humans to tap to produce electricity rather than looking for more fossil fuels which is fast depleting. Solar energy is a clean source of energy, helping in reduction of harmful environmental effects. While the production of components in a solar power system may cause pollution, it is very negligible considering 13 grams of carbon dioxide emission per unit of electricity produced through solar photovoltaic power plant versus the 1000 grams of carbon dioxide emission per unit of electricity produced through coal power plants. The Solar energy is the power source produced natural from the sun. There are two ways of power generated from the sun. One is the electrical energy produced from the sunlight. The other is through the heat from the sun that can be used to produce both electrical energy and thermal energy. The radiation from the sun or the sunlight is converted into electrical energy through solar photo voltaic panels. The solar photovoltaic panel is predominantly a semiconductor device which is made of silicon materials. The silicon when exposed to sunlight generates electricity. A variety of solar technologies has been developed and it has a lot more potential to grow to tap the full potential of solar energy.
SOLAR ENERGY – SIGNIFICANCE
Carbon dioxide is a natural constituent of air which constitutes around 250 – 350 ppm. But an increased level is a serious threat to the environment. Indian power generation capacity is close to 3, 50,000 MW out which close to 2, 00,000 MW is from the highly polluting coal based power plants. Every one unit of electricity produced from coal power plant emits 1000 grams of carbon di oxide into the environment causing serious climatic change threats. Besides humans, other organisms in the ecosystem too get affected. The generation of solar power, which is a green and renewable energy can mitigate the emission of carbon dioxide from power plants to a great extent. The solar power plants have the potential to replace the coal based power plants helping in leaving a better world for the generations to come. The solar photovoltaic power plants have negligible moving parts and hence there is negligible chance for wear and tear. This greatly reduces the operation and maintenance costs which is significantly higher in other non-renewable energy generation power plants. Even if all non – renewable sources of energy are utilized, the energy generated will be only equal a few days of energy output by the sun. The amount of electricity generated by burning fossil fuels since the start of the civilization will be less than the energy produced by the sun in 30 days. The use of solar energy will reduce carbon footprint, leading to a clean air and healthier environment. The economic impacts are very sustainable as it saves money and creates job.
TYPE OF SOLAR INSTALLATION
Solar installations can be done either in the roof top or on the ground. The ground mounted installations are usually for utility scale projects, where the power produced to is mostly sold to Government distribution companies. On the other hand, rooftop solar installations can be done on the rooftop of the premises. The power produced by the rooftop installations are used by the owner of the premises. The rate of installation of the rooftop solar installation has been growing steadily year on year, with Tamil Nadu leading at the end of the financial year 2017.
Solar Utility level capacity
As the table clearly shows, the capacity addition of the utility solar power plants have increased drastically. From 1842 MW in 2013, it has increased 16,203 MW in 2017 which is a tremendous growth with almost 100% year on year growth in the year 2017 from 2016. The utility level capacity addition in Tamil Nadu has also increase from 21 MW in 2013 to 1804 MW in 2017 with close to 32% year on year growth in 2017 from 2016.
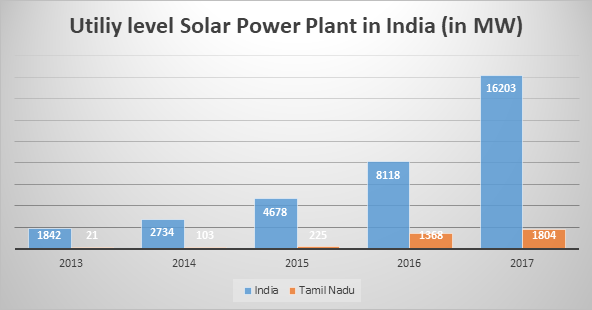
Source: Bridge to India reports on India solar map – 2013 to 2017
Solar Rooftop capacity
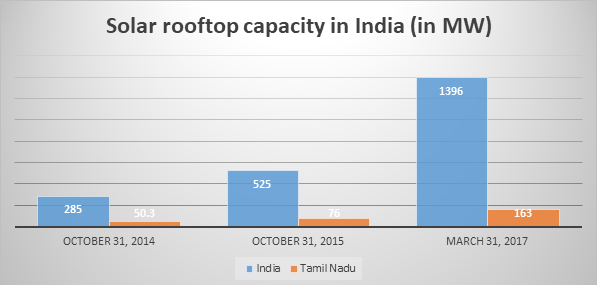
Source: Bridge to India reports on India solar rooftop map – 2015 to 2017
The rooftop capacity in India has grown from 285 MW in 2014 to 1,396 MW in the first quarter of 2017. The Tamil Nadu solar rooftop capacity has increased from 50.3 MW in 2015 to 163 MW in 2017. The market attractiveness in so high that there are 664 solar project developers in Tamil Nadu registered with the Tamil Nadu Energy Development Agency.
REDUCTION IN CARBON DIOXIDE EMISSIONS
India emits on an average 24, 54,968 KT of carbon di oxide annually. India is ranked fourth in the list of countries that emit carbon di oxide with a per capita emission of 1.9T. Solar power plant produces energy through renewable energy resource and eliminates carbon di oxide emissions. One electrical unit of solar energy produced reduces 1 Kg of carbon di oxide emissions that would be resulted from power generation from a coal plant. From the data above, it is very clear that the solar power plants has reduced the carbon di oxide emissions to a great level.
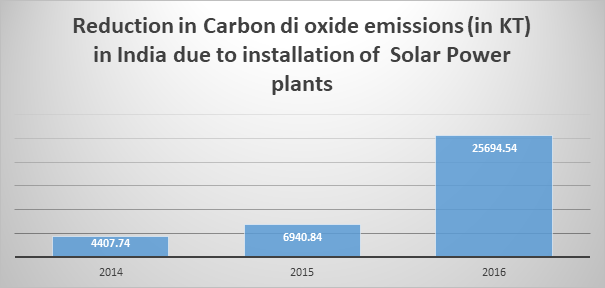
Source: Based on calculator in Solar Mango (https://goo.gl/ZUkUFL)
COST REDUCTION
The capacity addition of solar power plants has been increasing year on year. At the same time, the price of the solar power plants has been going downwards. Thanks to the huge year on year capacity additions, the market become very attractive opening competition among existing project developers and new entrants. By the going trend, the price is expected to come down further.
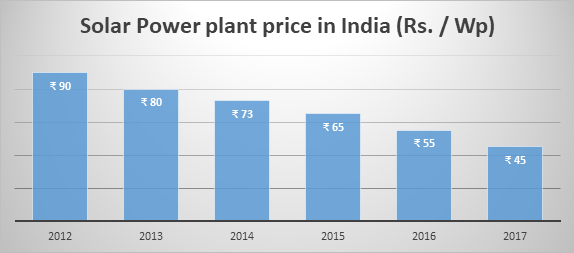
Source: Bridge to India reports on India solar rooftop map 2017
PROJECTIONS
By the end of 2021, the capacity addition in the utility scale is expected to be at 47,000 MW and the rooftop capacity is expected to reach 12,500 MW. This in turn translates to reduction of carbon di oxide which would have otherwise resulted in the emission of 87,000 KT of carbon dioxide from the coal plants.
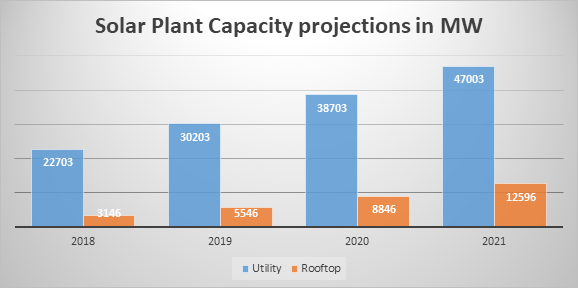
Source: Bridge to India reports on India solar rooftop map 2017
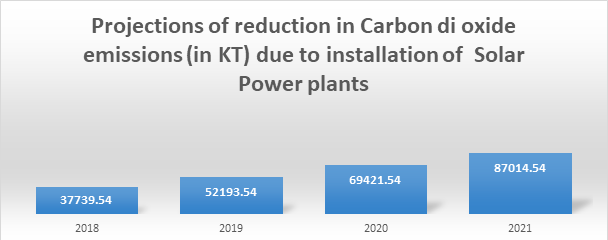
Source: Based on calculator in Solar Mango (https://goo.gl/ZUkUFL)
CONCLUSION
The power requirements will always be on the rise and the power generation capacity will also be increasing year on year to meet the demands of ever increasing power. It is wise to build capacities in a sustainable way so that the unfavorable climatic changes can be mitigated drastically. Hence it could be concluded that usage of solar energy as an alternative source would help us to leave a clean, safe and healthier world for our future generations.